ChestLink is the first fully autonomous AI medical imaging product with a CE mark. ChestLink identifies CXRs with no abnormality and produces finalized patient reports without any intervention from the radiologist, reducing radiologist workload and enabling them to focus on cases with pathologies.
AI autonomy in medical imaging is not driven by the technology, but by the current systematic healthcare shortcomings the platforms aim to address. It is safe to say that in developed countries the radiology departments are understaffed by 1/3. According to the World Health Organization, 2/3 of the world population does not have access to diagnostic medical imaging
By autonomously reporting on CXRs with no abnormalities where it is highly certain of the results, ChestLink may automate from 15% to 40% of daily reporting, freeing up radiologists to report on cases that feature pathologies.

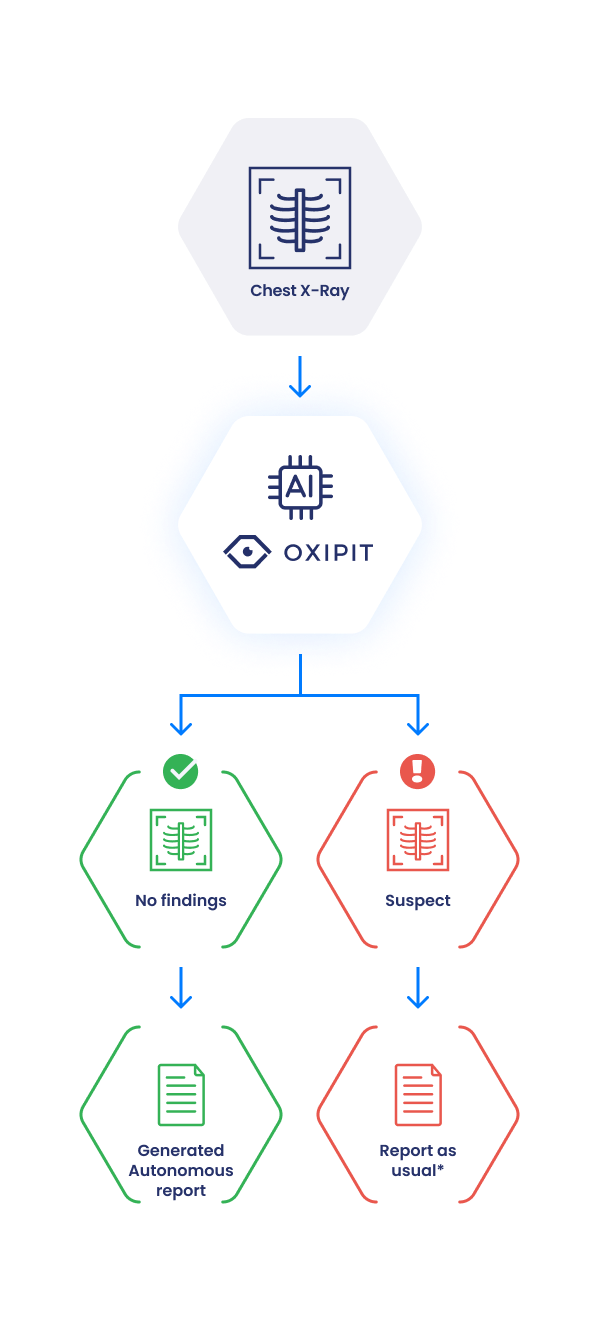
*- On demand Oxipit could send preliminary reports, heatmaps, priority label or pathology label to improve the radiologist’s experience.
ChestLink deployment begins with retrospective analysis of customer CXR data. The scope of analysis may include a couple of years worth of chest X-rays and radiological reports. At this stage ChestLink estimates what share of no-findings X-rays can be determined with high certainty – making this subset available for future autonomous reporting. In addition, potential false-negatives and report mismatches are analyzed on a case-by-case basis.
The aim of retrospective analysis stage is:
At this stage ChestLink operates ‘in the background’, shadowing the radiologist. The platform marks no-findings X-rays and compares these reports with the reports by the radiologist (whether the radiologist also marked this CXR as ‘no-findings’). Any mismatches are highlighted and analyzed by the Oxipit team and the team at the medical institution.
At this stage ChestLink begins to autonomously report on no-findings chest X-rays, where the platform is highly-certain that the patient is healthy. The same cooperation procedures – including analytical auditing tools as well as periodic audit updates put in place during the prospective analysis stage – are also utilized at this stage.
Automate up to 40% of reporting workflow
Save radiologist time by automating a significant portion of high-confidence healthy patient reports, where radiologist export input adds little clinical value.

Shift radiologist focus on cases with pathologies
By reducing workload, enable radiologists to shift their expert attention on cases with featured pathologies.
High confidence reporting
ChestLink will only produce automated reports for chest X-rays, where it is highly confident that the images feature no abnormalities. This allows the sensitivity metric to be higher than 99%.

Accountability of operations
ChestLink analytical dashboard is an integral part of autonomous AI operations. It allows stakeholders to trace back and evaluate every case reported by the AI.

Fully GDPR Compliant
ChestLink adheres to strict privacy regulations. All identifiable data is anonymized and the platform operates onsite.
ChestEye Quality builds upon the vanguard capabilities of the ChestEye imaging suite, which supports 75 most common radiological findings covering 90% of pathologies encountered at a medical institution on a daily basis.
Read the full list of ChestEye Supported Findings